

 “It’s not always possible to find a reliable, cooperative partner straight away; therefore we started to work with Arkbauer on small project. After our first project Arkbauer proved to be reliable experts in software development, who we can trust not to cause any headaches.”
“It’s not always possible to find a reliable, cooperative partner straight away; therefore we started to work with Arkbauer on small project. After our first project Arkbauer proved to be reliable experts in software development, who we can trust not to cause any headaches.” Web portal Visidarbi.lv is one of Latvia’s leading job search engines and aggregators displaying more than 20,000 job ads every day. Visidarbi.lv enables job seekers to search for vacancies posted on thousands of websites all in one convenient location. Employers can also advertise jobs directly on the site.
Tasked with processing tens of thousands of job ads daily, the Visidarbi.lv website started to suffer performance issues that negatively impacted on the user experience. Our task was to analyse the system and suggest ways to resolve these performance issues.
To provide the best analysis, we wanted to understand the original system requirements and review the current architecture. Basic requirement study documents helped us understand the main features found in the system. However, no documents related to the system architecture existed. Instead, we explored the source code and site itself to reveal the underlying architectural design.
The system is built using Symfony 2.1 running on Nginx with PHP 5.4. It used MySQL 5.5 for data storage and Sphinx as a search engine. All this was running on a single CentOS Linux server with 6x cores and 12GB RAM.
First we tried to profile the system and find the bottlenecks with a limited amount of data. This proved very hard as the code available under VCS was different from that running in the production environment and staging. We also found that some parts of the code were just not working at all.
We were given access to the production server so we were able to analyse its load, memory and CPU consuming processes. At this point it was already clear that the main issue came from SQL queries as the mysqld process was utilizing more than 400% of the server’s CPU with relatively small numbers of visitors browsing the site.
Given the fact that the same server was being used as a staging server with several site instances, it was not clear whether the database related issues were the key problem. So, next we decided to perform profiling in the production environment. We used Facebook’s XHProf profiler to find bottlenecks in the Visidarbi.lv system. Due to the fact that profiling itself adds an additional 10% overhead performing calculations and collecting data, we enabled it only for our own IP address leaving actual site visitors unaffected.
The very first profiled search request results confirmed our findings – more than 90% of the time taken to generate a response was spent performing queries. We profiled other site sections as well and they all showed pretty much the same results.
So we found the main bottleneck, what next? First, we enabled MySQL slow query log. We configured it to log all queries that take longer than 3 seconds to execute even though it’s considered best practice to have queries executing in less than 0.1 seconds. We gave slow query log 24 hours before analysingthe slow queries and making some assumptions. In the meanwhile we analysed other parts of the system to provide an overall picture.
As of 26th February 2016 PHP 5.4 was used, which is around a year after support ceased by the PHP development team.
Suggestion: migrate to PHP 7
As of 26th February 2016, Symfony 2.1 was used, which has not been supported since November 2013.
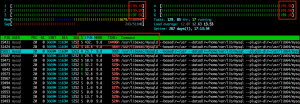
CentOS Linux server with 6x cores and 12GB RAM is enough to handle the expected load. However, the current website’s setup is utilizing almost all the server’s resources (see image below) with even small numbers of visitors.
As of 26th February 2016, MySQL 5.5.43 has been used and is currently supported and maintained.
After profiling we concluded that performance issues are directly related to the database and its queries.
The MySQL database process utilizes more than 400% of server’s CPU capacity when its maximum is 100% * 6 (number of cores) = 600%. For optimal system performance 1/3 of the server’s resources should be reserved (not used) for high load peaks.
We enabled MySQL slow query log feature to capture SQL queries executing for more than 3 seconds. In 24 hours there were 69,000 such queries captured. The majority of those were queries related to search keyword statistics that take 1.5 to 2.1 minutes to execute.
Analysing the most time consuming queries we concluded that they include search e.g. “LIKE ‘tu%’”. MySQL database is not suitable for search related operations. Nowadays dedicated search engines are being used for such tasks, especially for Full Text Search needs.